
Electricity
Learning physics
and chemistry
easily and freely - Science for elementary school, middle school and
high school
Free online electricity lessons for elementary school, middle school and high school.
Electrical components
Diodes
1) Diodes and LED
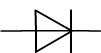
Diodes are two-terminal components.
There are two kinds of diodes:
- The simple diodes.
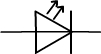
- Light emitting diodes (LEDs) that operate as simple diodes but emit light when electric current passes.
| Diode standard symbol | LED standard symbol |
 |
 |
Red or green LEDs are very commonly used in electrical devices (televisions, computers etc.) and serve as controls that indicate operating condition or standby.
2) The fragility of diodes
Diodes are very vulnerable two-terminal components that are easily damaged by excessive electrical current. So they are never used alone and often protected by two-terminal components called resistors whose roles is to limit the electric current.
Standard symbol of a resistor:

American standard symbol:
3) Diodes and electric current
Diodes and LEDs are polarized so they don't behave the same way if electric current is reversed.
Example:
We realize two circuits that differ only in the sense of connection of a LED
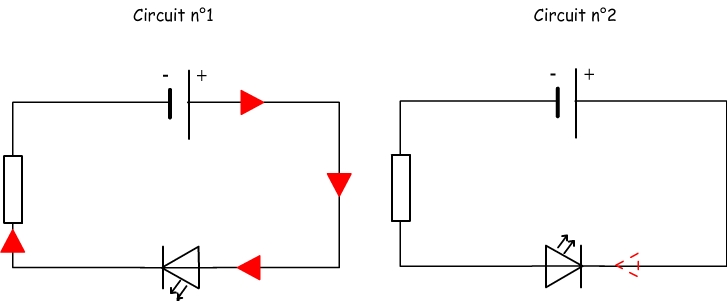
We can observe the LED lights in circuit n°1: it is traversed by an electric current.
We can observe that the LED remains off in the circuit n°2: no current flows.
In circuit 1 we say that there's a bypass LED.
In circuit 2 way there's a blocking LED.
We can distinguish a bypass diode and a blocking diode on a diagram by comparing the current direction and the diode symbol: when they are pointing in the same direction there's a bypass diode.
| A bypass LED | 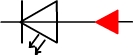 |
| A blocking LED | 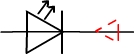 |
Comment:
A bypass diode can be compared to an open switch whereas a blocking diode can be compared to a closed switch.

| Science class |
Chemistry Electricity Optics Mechanics |
| Electricity lessons |
| Electrical
components -Two-terminal electronic components - Basic electrical components - Diodes - What's a resistor ? - How to determine a resistor value ? - Resistors effects in circuits - How to use a resistor ? - Characteristic curve of a resistor How to build simple circuits and draw diagrams - How to build a basic electrical circuit - How to draw diagrams of electric circuits The electric current - Conductors and insulators - Direction of electric current in a circuit - The dangers of electricity - Current intensity - units how to measure current ? The Voltage - The voltage and its units - How to measure a voltage ? - Voltage in open and closed circuits - Rated current and voltage for a lamp Alternating voltage and current - Alternating currents effects on led - What are alternating current and voltage ? - Periodic alternating voltage and its properties - Oscilloscope - Oscillogram - Frequency - Measuring RMS voltage with a voltmeter Serie circuits - What's a serie circuit ? - Series circuit properties - Short circuit in series circuit - Current law in series - circuits - Voltage law in series circuits Parallel circuits - What's a parallel circuit ? - Some parallel circuits properties - Short circuits in parallel circuits - Nodes and branches in parallel circuits - Current laws in parallel circuits - Voltage laws in parallel circuits Laws of electricity - Ohm's law - Current laws in series circuits - Voltage laws in series circuits - Current laws in parallel circuits - Voltage laws in parallel circuits Generating electricity - Voltage for coil wires What is an alternator ? - Alternating currents and voltages - Generating electricity in power plants Electric power and energy - Electric power and power rating - Electric power received by an electrical device - Electric power consumption by an electrical device - Relationship between - Electric power and energy |
|
|
©2021 Physics and chemistry


