
Chemistry
Learning physics
and chemistry
easily and freely - Science for elementary school, middle school and
high school
Free online chemistry lesson for elementary school, middle school and high school.
Metals
Electrical conductivity of solid materials
Solid materials can be classified into two main categories:
- Electrical conductors that can be crossed by an electric current.
- Insulators that don't conduct electric current.
To determine whether a material is conductive, a test of conductivity can be performed using the following circuit:
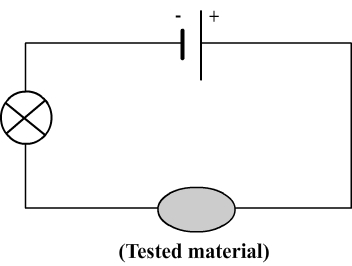
The principle of this test is simple:
- If the bulb lights, it indicates that the electric current flows then the material is conductive.
- If the bulb doesn't light, it indicates the electric current doesn't flow so the material is insulative.
Test results:
| Tested materias | Test results: |
| Iron | Conductor |
| Zinc | Conductor |
| Aluminium | Conductor |
| Copper | Conductor |
| Copper sulfate powder | Insulator |
| Salt powder | Insulator |
| Wood | Insulator |
| Plastic | Insulator |
This test permits to show that only metals are conductors and most other solid materials are insulators.
This characteristic can be explained by their microscopic properties

©2021 Physics and chemistry


