
Chemistry
Learning physics
and chemistry
easily and freely - Science for elementary school, middle school and
high school
Free online chemistry lesson for elementary school, middle school and high school.
Mass and volume
Measuring volume with a graduated cylinder
1) Which container can be used to measure volume ?
A water volume can be measured with a graduated container as a beaker, flask, or conical measure.
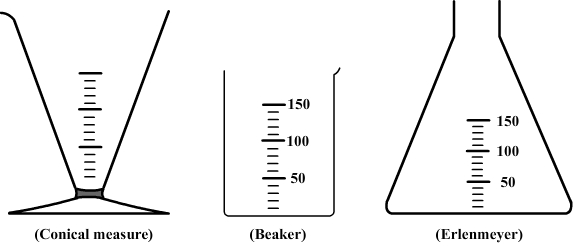
However, their indications of volume are approximations and for a higher accuracy a graduated cylinder is more suitable.
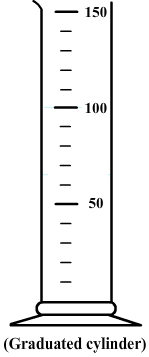
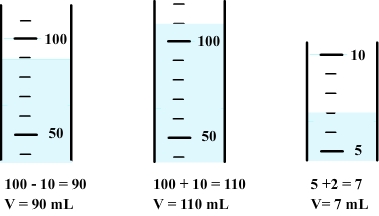
2) Method for using a graduated cylinder
Step 1:
There are some graduated cylinders of various capacities (5 mL to 500 mL in general), each with its own system of graduation.
Therefore, the volume corresponding to each division must first be determinate.
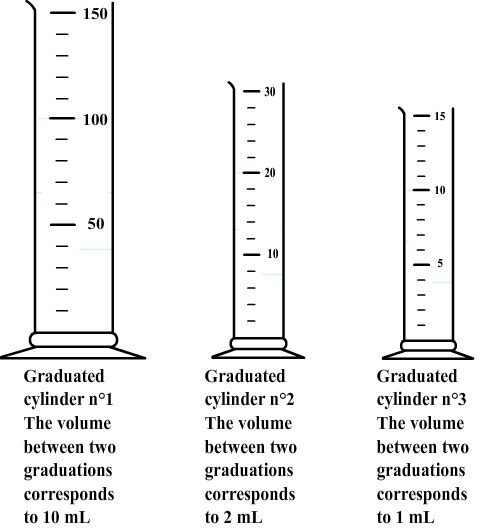
Step 2:
To measure volume, the graduation the closest to the free surface of the liquid must first be determined.
The observer must then set his eyes at the same level as the free surface.
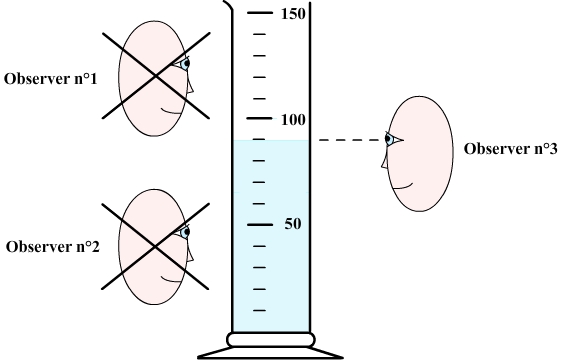
Step 3:
Volume can be calculated using previous informations.
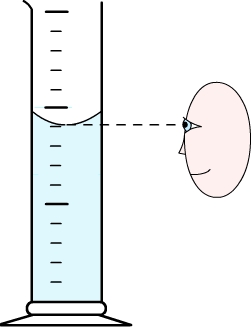
Comment:
Due to the capillary action, water tends to be attracted by the walls of its container. This phenomenon is negligible for wide containers but in narrow containers it can be observed that the surface becomes round (the surface is curved).
To correctly determine the volume of liquid then you should take as a reference the lowest point of the curved surface.

©2021 Physics and chemistry


